By: Inoljt, http://thepolitikalblog.wordpress.com/
The New York Times posted a very interesting map of Afghanistan’s recent election.
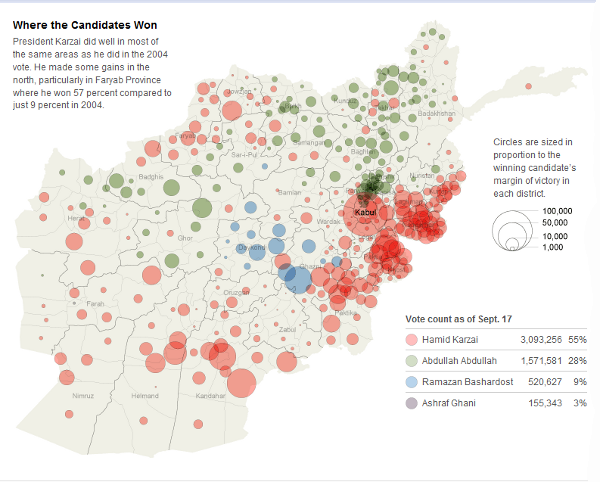
Before continuing, I must note that my purpose is not to question whether irregularities or fraud might have denied Abdullah Abdullah victory; I am simply analyzing the data as it appears.
There’s a lot of data here, and interpreting it is fairly difficult; few people know much about Afghan politics and demographics. This map indicates the margins each candidate won. Kabul is the big red circle. In total, Karzai won 55% of the vote, essentially doubling the vote of the second-closest candidate.
Compared to a similar maps of U.S. elections, several things stand out. The first is the extent to which polarization is apparent. Afghani society is very clan-based, and elections can reveal polarization like nothing else.
At the point most politicians win an election by more than 20%, maps like the one above tend to consist of something like below:
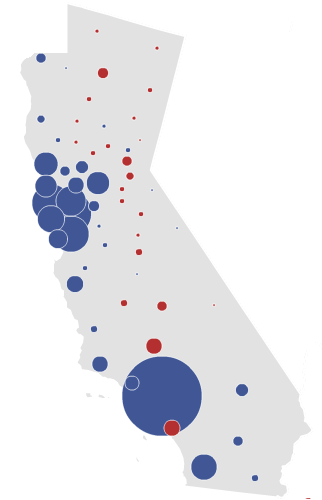
This is Barack Obama’s 24.03% landslide in California. Compare it to Karzai’s 27% victory: one might be forgiven for concluding that out of the two elections, Karzai did worse.
(Many) more maps below the fold.
Notice too that Ramazan Bashardost, who won only 9% of the vote, shows up as a presence on the map. This indicates a very regional candidacy, like that of William Wallace. Candidates who win 9% of the vote nearly never show up on any type of election map; Ross Perot, for instance, won less than a dozen counties with his 18.9% of the vote.
Abdullah Abdullah was also a regional candidate, as the following map reveals:
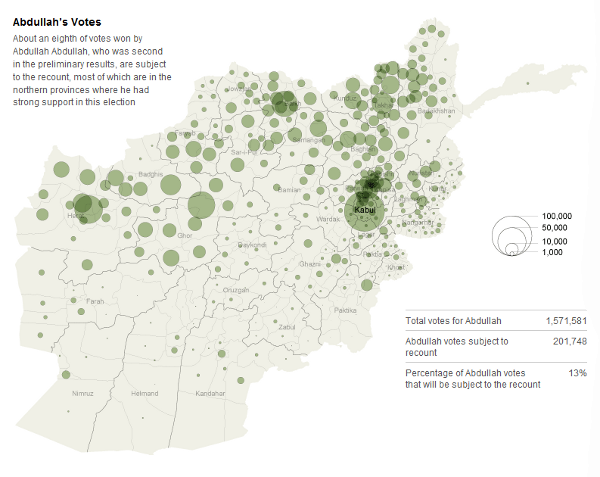
Mr. Abdullah is almost entirely limited in support to the north; very few Pashtuns in the south seem willing to vote for him. This was not the case with Karzai; his total vote looks far more homogeneous:
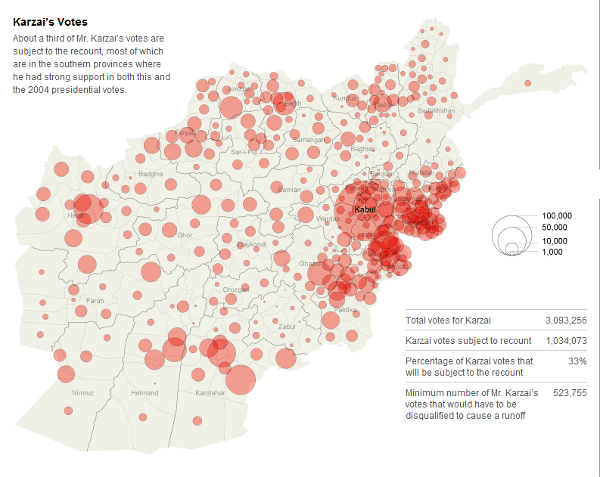
There are several American states that the results Afghanistan’s election can be comparable to. The victor wins the one major city along with a number of more rural areas, although the opposing candidate summons strong support in one region. In this respect, Karzai’s victory resembles the coalition Bill Clinton assembled in many Appalachian states, such as Missouri and Tennessee (his loss in Oklahoma also bears similarities to Afghanistan). Recent presidential elections, on the other hand, generally do not follow this pattern; cities and rural areas rarely vote together (and cities never vote Republican). After Bill Clinton, only Obama’s Iowa victory comes to mind as a state with a “Karzai” coalition. Note that in all this states, the winner’s margin was far less than Karzai’s 27%.
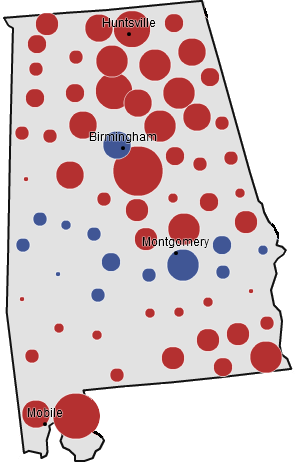
The place that Afghanistan’s election calls most to mind, however, is Alabama. Both are extremely polarized: Afghanistan by tribe, Alabama by race. Republicans regularly win landslides in Alabama, yet always lose a particular region – the Black Belt – just as Karzai lost many Afghan areas despite his strong performance. Accusations of fraud have severely tainted the Karzai “landslide,” just as fraud of a different type was practiced in Alabama for many decades. Finally, both areas are extremely poor and will likely remain so during the forseeable future.