I have been working on (with some much appreciated help from pl515) a concept I’m calling PBI or Party Brand Index, as a replacement for PVI. PVI (Partisan Voting Index), which is measured by averaging voting percentage from the last two presidential elections in each house district, and comparing it to how the nation as a whole voted, is a useful shorthand for understanding the liberal v. conservative dynamics of a district. But in my opinion it falls short in a number of areas. First it doesn’t explain states like Arkansas or West Virginia. These states have districts who’s PVI indicates a Democrat would be in a hard position to win, never the less Democrats (outside of the presidency) win quite handily. Secondly why is that the case in Arkansas but not Oklahoma with similar PVI rated districts?
Secondly PVI can miss trends as it takes 4 years to readjust. The main purpose of Party Brand Index is to give a better idea of how a candidate does not relative to how the presidential candidate did, but rather compared to how their generic PARTY would be expected to perform. I’m calling this Party Brand Index.
My best case for arguing against PVI is Indiana. Bush won Indiana quite easily in 2000 and 2004. The PVI of a number of it’s districts showed them to be quite Red. Yet in 2006 democrats won several districts despite their PVI’s. Also Obama won Indiana in 2008 a state, which based on the make up of the districts PVIs, made little sense. I therefor chose Indiana as my first test case for PBI.
Indiana also had a number of other oddity that made it an interesting test case. Indiana has Senators from opposite parties that each won election by large blowouts. Lugar’s in particular was enormous as he was essentially unopposed. Indiana also had a number of districts that flipped in the 3 election cycle expanse that I’m examining. Finally it makes the best case for why PVI can be misleading.
To compute PBI I basically did the following. I weighed the last 3 presidential elections by a factor of 0.45. Presidential preference is the most indicative vote since it’s the one politician people follow the most. The POTUS is the elected official people identify with or despise the most, thus illuminating their own ideological identification. I then weighed each house seat by 0.35. House seats are gerrymandered and the local leader can most closely match their districts make up in a way the POTUS can’t. So even though they have a lower profile I still gave them a heavy weight. Lastly I gave the last two Senate elections a weight of 0.2. Senatorial preference can make a difference, although I think it’s less than that of the President or the House members. Also (more practically) because I have to back calculate (estimate) Senate result totals from county results, a smaller number helps lessen the “noise” caused by any errors I may make.
I was then left with this chart:
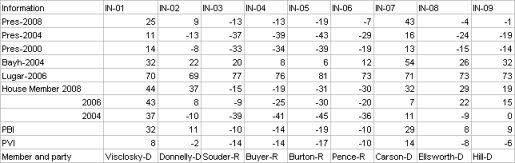
I now began to look at the results. Under my system Democratic leaning have a positive number, the GOP has a negative number. Donnelly in the Indiana 2nd is a perfect example of my issues with PVI. Under PVI Donnelly is in a Republican district with a PVI of -2. But look at how democrats have recently performed in this district. In 2008 Donnelly won reelection by 37%! Obama won this ditrict by 9 points, and Bayh won it by 22%! Does this sound like a lean GOP district? Under PVI it is, under PBI it’s not it’s a +11 democratic district.
I then decided to go all Nate Silvaish and gave more recent elections a greater weight. I gave an addition 5% weight to each election as it got closer to the most recent election. To be honest I pulled 5% out of my dairy air but Nate gave a similar weighting to poll results as fresher ones came in 2008, so I copied this formula. This resulted in the following:
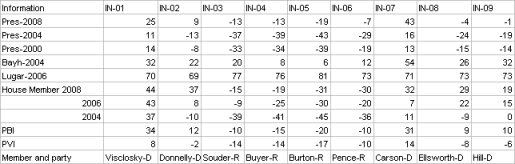
The next issue I decided to tackle was to develop a way to weight for incumbents. The reelection numbers for incumbants is so high it would be a mistake to weight a district soley on the fact that an incumbat continues to get elected. There is a long list of districts that have PVI that devate from their incumbant members, whom none the less keep getting elected. These disticts then change parties as soon as the incumbant member retires. This is evidence that incumbancy can disguise the ideology of voters in a district.
I decided on a weight of about 7% for House members. I remember reading that incumbency is worth about 5-10%. Also Nate wrote in a 538.com article that a VP pick from a small state was worth about a 7% swing, a house seat could in fact be thought of as a small state, that seems as good a number as any to start from. Conversely I will deduct 7% from an incumbents win. I think this will score them closer to the natural weight of a district. By the way I’m weighting the win 7% less, not actually subtracting 7% from the number. Open seat races will be considered “pure” events and will remain neutral as far as weighting goes. A seat switching parties will also be considered a neutral event. The 1st defense of a seat by a freshman house member will be given a weighting of 2%. The toughest race for any incumbant is their 1st defense. I decided to adjust for this fact. Note: Indiana’s bloddy 9th was a tough call a case could be made that when a seat keeps flipping, and the same two guys run 4 straight times in a row each election should be a neutral event.
Senate weighting will be as follows. In state with a single House seat the Senate seat will be weighted the same as a house. In states with mutiple seat, the Senate will get a wighting of 2%. Nate Silva stated that a VP pick in a large state is worth this amount. An argument could be made for a sliding scale of Senate weighting from 2-7%, this added complexity may be added at a later date. I will give incumbant presidents a 2% weighting, until I get better data on how powerful a “pull” being the sitting POTUS is, I will give them the same weighting as a senator.
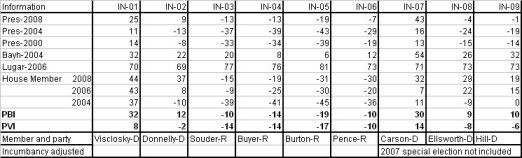
The main purpose of Party Brand Index is to give a better idea of how a candidate does not relative to how the presidential candidate did, but rather compared to how their generic PARTY would be expected to perform. I’m calling this Party Brand Index.
______________________________________
The last major issue is how to deal with the “wingnut” factor. Sometimes a politician like Bill Sali (R-Idaho) or Marylin Musgrove (R-CO)lose because their voting record is outside of the mainstream of their district. I decided to try and factor this in.
First I had to take a brief refresher on statistics. I developed a formula based on standard deviations. Basically I can figure out how much the average rep deviates from their district. If I then compare where a reps voting pattern falls (in what percentile) and compare it to their district’s PVI, I can develop a “standard deviation factor”. Inside the standard deviation will get a bonus, outside a negative.
For example, if Rep X is the 42 most conservative rep, that would place her in the 90th percentile. But if her district’s PVI was “only” the in the 60th, their is a good chance her margins would be effected. Using a few random samples I found most reps lie within 12% of their district’s PVI.
Using these dummy numbers I then came up with this.
SQRT[(30-12)^2 /2] = about 13%Her factor would then be 100 – 13 = 0.87.
So her victory margin would be weighted by 0.87 because she is more than 12% beyond her acceptable percentile range it making the victories in her district approximate 13% less “representative”.
My theory yields the following formula:
If rep’s voting record is > PVI then
100 – SQRT[({Record percentile – PVI} – Standard PVI Sigma)^2 /2] = factor
else if rep’s voting record < PVI
100 + SQRT[({Record percentile – PVI} – Standard PVI Sigma)^2 /2] = factor
To really do this I need to compute the standard deviation for all 435 reps, which is a pretty large undertaking. Instead I will do a google search to see if anyone has already done this. If not well it will take some time. But this would deal with the wingnut factor. Since politician tend to vote relatively close to their districts interest (even changing voting patterns over time) this may not be a major issue. But developing this factor may eventually allow the creation of a “reelection predictor”, so I am still going to work on it.
One last note, the corruption factor (for example Rep. Cao (R-LA) beating former Rep. Jefferson) is outside of any formula I can think of. The only saving grace here is that because my formula uses several elections, the “noise” from a single event will eventually be reduced.
Next Up: Colorado ( have the data done already) and Virginia
I’m impressed by all the effort you put into this!
My only caution is that, while PVI can have the effect of seeming to underrate a Democrat’s chances in certain districts, PBI may overestimate it. So it probably makes sense to look at both numbers.
In the back of my mind I have a way of averaging the two figures. If the PVI is + Republican but the PBI is + Democratic the best candidate is a blue dog Democrat. The reverse is true for a + Democrat PVI, + GOP district a Rockefeller Republican would be needed.
you would have to individualize if you’re taking into account house performances, sometimes people are merely unopposed or running against a nobody. I think 7% is only valid instances with a valid opponent. You see fundamentally you are assuming all opponents of incumbents are the same, and that is absolutely untrue, so by even adding that addition to your calculations you’d have to create a much larger system to better match the quality of opponents, maybe a tier system, or, more simply, just remove that altogether, though that would definitely hurt accuracy. Forming a tier system of how much to subtract would be best. If unopposed by a major party, subtract 10-15, and then base the rest on fundraising, as fundraising is usually a good indication of how strong and active a local campaign is and how much it will be able to get out its message. Perhaps 5 tiers based on fundraising would be good idea.
In addition I think that should remove weight from House seats, which are intensely local and have candidates able to fit more time to their districts and specializing to them, and instead add in the Gubernatorial elections, as though are high profile statewide races, similar to a Presidential race, and it would show the base inclination. Right now your PBI’s are too Democratic. I would go with a .5 Presidential, .2 Senate .15 gov, and .15 House metric, incorporating that tier system of candidate quality into your winning margins for gov, house and Senate.
That would bring the PBI’s down a bit and show a more realistic version of Indiana. Yours would appear to have a Generic Party advantage for Democrats, while Indiana is still obviously a tough, fairly conservative state that is baseline favorable to Republicans right now. It will change, obviously, demographically Republicans are doomed. They rely on the 65+ demographic which votes nearly 70% Republican and is the most reliable turnout. Democrats have an overwhelming advantage on voters under age 25, 2:1, and as they get older and start voting more reliably, while the 65+ group begins to die out and dwindle in size, the state will become reliably Democratic.