This is the last part of a series of posts analyzing competitive Senate elections in blue states. It is the second section of two posts focusing on the greatest state in the union (otherwise known as California). The first part of the series can be found here.
Suburban SoCal
Southern California (SoCal, in short) is where the battle for California will be won or lost. Ms. Fiorina must accomplish two tasks in the region.
First, she must clean the clock in the suburban counties outside Los Angeles.
More below.
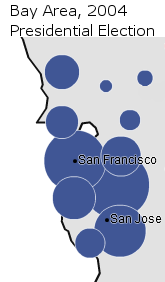
It is in places like Orange County, San Diego, and the Inland Empire that the votes to counter the Democratic bases in the Bay Area can be found. In the 2008 presidential election, there were one million more votes cast in the six SoCal counties above (excluding Los Angeles) than in the entire Bay Area.
This task is not too difficult. Unlike liberal NorCal, the suburbs in this region are more like the rest of the United States in their political leanings; in fact, they are probably more conservative than the median. Orange County and San Diego County are nationally known as conservative bastions (although they are not as red as in the past). Ms. Fioina probably needs to win above 60% of the vote in both counties. Historically, Republicans have often done this. The trouble is with Los Angeles.
Los Angeles
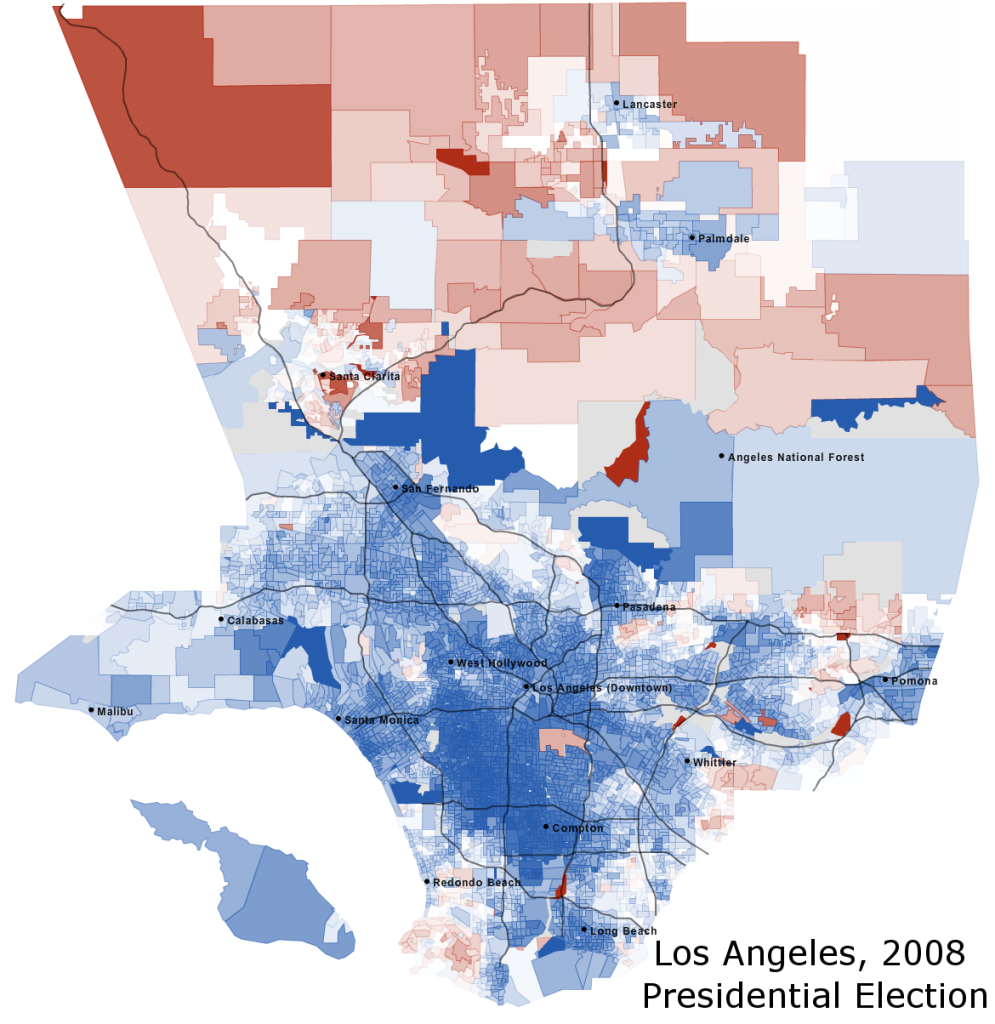
Ms. Fiorina’s second task is to run closely in Los Angeles. It is here that Republicans face their greatest challenge. Los Angeles – sprawled, extremely populous, and arguably more diverse than even the Bay Area – constitutes a Democratic stronghold. President Barack Obama ran off with 69.2% of the vote here; Senator John Kerry took 63.1%. Ms. Fiorina must reduce this Democratic margin to within the single-digits.
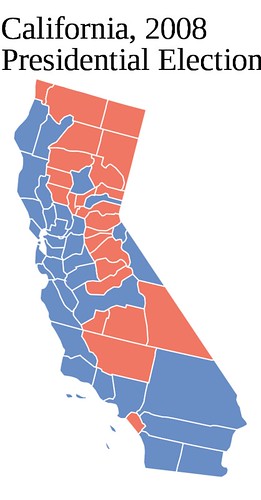
The math here is simple. There are just not enough Republican votes in Central Valley, the Orange County-San Diego metropolis, and the Inland Empire to offset the Democratic bastions of the Bay Area and Los Angeles. Republicans must therefore break one of the two strongholds. It is impossible to do this in the Bay. So the choice must be Los Angeles.
The key are the outer, wealthier suburbs within Los Angeles county. Some are liberal Hollywood areas, typified by Congressman Henry Waxman’s 30th congressional district. Republicans probably cannot win these. Others are more conservative and even voted for Senator John McCain (see, for instance, the patches of red north of Pomona and south of Redondo Beach). Ms. Fiorina will have to expand upon this core and win places like the San Fernando Valley and Pasadena – suburbs which rarely vote Republican.
Conclusion
When the voting booths close and the precinct results start pouring in, look at Los Angeles County. Ms. Fiorina’s performance there will be most indicative of her overall strength. If Democrats are winning the county by double-digits, then she is in trouble. Conversely, if their margin is less than five percent – or if Republicans are winning the county – then Republicans are in good shape. A Democratic margin between five and ten percent signifies that a long night is ahead.
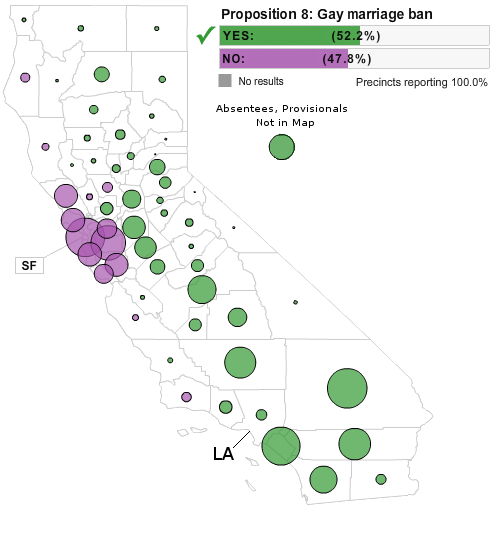
On a state-level basis, modeling a close Republican victory is somewhat difficult; Republican candidates haven’t won a close race for a long time in California. There is, however, a substitute that fits well:
These are the results of the famous Proposition 8, which passed by a 4.5% margin. On a county-by-county basis, a Fiorina victory will probably look quite similar to this. There are minor differences; the margins in Orange and San Diego Counties would probably be greater; Republicans probably wouldn’t win Los Angeles County.
Overall, however, the picture would not be too different. Heavy margins from the SoCal suburbs and Central Valley counter Democratic strength in NorCal, while a strong Republican performance in Los Angeles dilutes Democratic margins there.
There is one final complication for Republicans. California constitutes the most diverse state in the country; winning minorities is a must. The Republican Party is not very good at this, which why California is a blue state today. It must change this, if candidates like Ms. Fiorina are to win the state.
Some minorities are easier to win than others. Blacks are most loyal to the Democratic Party, but they number only 6.2% of the state’s population. While more numerous Asians and Latinos do not vote their numbers (their share in the voting electorate is slightly more than half their share of the overall population), their votes are easier to get.
Here Proposition 8 is less useful as a guide. In Los Angeles County, for instance, all of South Central voted for the proposition. Unless Republicans start winning Compton and Watts, they will have to find support from a different section of California’s majority-minorities.
Winning minorities constitutes a novel challenge to the Republican Party; until now it has drawn an ever-increasing percentage of the white vote to offset increasing numbers of minorities. This is no longer possible in places like California. If Republican candidates like Carly Fiorina and Meg Whitman are to win the state, they will need to envision a new strategy.
(Note: Credit for several edited images goes to the LA Times).
–Inoljt, http://mypolitikal.com/