By: Inoljt, http://mypolitikal.com/
The recent mid-terms were, by all accounts, very bad for Democrats. They lost 63 seats in the House of Representatives and 6 seats in the Senate. In many ways things were worse than in 1994, when Republicans won landslide victory.
There is another analogy to 1994, however, which will probably make Democrats happier. President Bill Clinton, after devastating mid-term losses, went on to win a comfortable re-election campaign. Can Mr. Obama do the same?
The book “The Keys to the White House,” by Professor Allan J. Lichtman provides a fascinating answer. Mr. Lichtman argues that the results of a presidential election can be predicted months or years beforehand by a series of thirteen “keys.” According to this theory, if the incumbent party or current president captures a certain number of “keys”, it will win the election. Otherwise it will lose.
More below.
This can readily be applied to the 2012 presidential election. Here are Mr. Lichtman’s exact words:
The Keys to the White House are stated as conditions that favor reelection of the incumbent party. When five or fewer statements are false, the incumbent party wins. When six or more are false, the incumbent party loses.
Key 1: Incumbent-party mandate – After the midterms the incumbent party holds more seats in the U.S. House of Representatives than it did after the previous midterm elections.
Key 2: Nomination-contest – There is no serious contest for the incumbent-party nomination.
Key 3: Incumbency – The incumbent-party candidate is the sitting president.
Key 4: Third party – There is no significant third-party or independent campaign.
Key 5: Short-term economy – The economy is not in recession during the election campaign
Key 6: Long-term economy – Real annual per-capita economic growth during the term equals or exceeds mean growth during the previous two terms.
Key 7: Policy change – The incumbent administration effects major changes in national policy.
Key 8: Social unrest – There is no sustained social unrest during the term.
Key 9: Scandal – The incumbent administration is untainted by major scandal.
Key 10: Foreign or military failure – The incumbent administration suffers no major failure in foreign or military affairs.
Key 11: Foreign or military success – The incumbent administration achieves a major success in foreign or military affairs.
Key 12: Incumbent charisma – The incumbent-party candidate is charismatic or a national hero.
Key 13: Challenger charisma – The challenging-party candidate is not charismatic or a national hero.
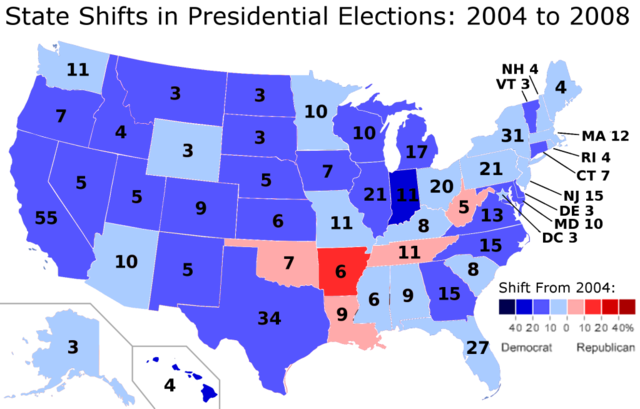
A year before the 2008 presidential election, Mr. Lichtman used these keys to confidently predict that Democrats would win the coming election. Seven of the keys – the incumbent-party mandate, the nomination contest, incumbency, policy change, foreign/military failure, foreign/military success, and incumbent charisma – were going against the Republican Party at that point. As the election went on, three other keys turned against them: short-term economy, long-term economy, and challenger charisma. The Republican Party thus went into the 2008 presidential election with ten of the thirteen keys turned against them. In this context, it is not surprising that Senator John McCain lost.
Let’s take a look at how the keys are stacking up in 2012:
Key 1: Incumbent-party mandate – After the midterms the incumbent party holds more seats in the U.S. House of Representatives than it did after the previous midterm elections.
Democrats would have had to lose twenty-three or less seats for this statement to be true. That definitely did not happen. This statement is FALSE.
___________________
Key 2: Nomination-contest – There is no serious contest for the incumbent-party nomination.
Nobody has the stature to contest Mr. Obama in the Democratic primary, even with recent liberal unrest over his tax cut deal. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 3: Incumbency – The incumbent-party candidate is the sitting president.
The Democratic candidate is indeed the sitting president. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 4: Third party – There is no significant third-party or independent campaign.
Ralph Nadar and 2000 effectively killed-off third-party candidacies for a generation. At the moment, 2012 isn’t looking any different. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 5: Short-term economy – The economy is not in recession during the election campaign.
This is a tough one – the economy probably won’t be in recession in 2012, but it certainly could feel like a recession. Given that so much of Democratic troubles stem from the short-term economy, for the moment this statement will be FALSE.
___________________
Key 6: Long-term economy – Real annual per-capita economic growth during the term equals or exceeds mean growth during the previous two terms.
This particular statistic is also tough to find, but we can certainly infer some things from just looking at real GDP. According to my calculations, Mr. Bush averaged 2.0% real GDP growth (the relevant websites are here and here). That’s pretty low, but real GDP growth was – 2.6% in 2009 because of the recession. The first quarter of 2010 was 3.7%. The second quarter was 1.6%. The third is estimated to be 1.5%. So real GDP growth under Mr. Obama has been something like an average – 0.5%. Over the eight quarters left until November 2012, real GDP would have to grow by something like an average 4.2% for Democrats to win this key. That’s just within the conceivable bounds of possibility, although it’s quite unlikely. This statement is UNKNOWN – LEANING FALSE.
___________________
Key 7: Policy change – The incumbent administration effects major changes in national policy.
Health care definitely was a major change in national policy. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 8: Social unrest – There is no sustained social unrest during the term.
Tea Party shenanigans don’t count as “sustained social unrest.” This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 9: Scandal – The incumbent administration is untainted by major scandal.
The Obama administration has not yet had a major scandal. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 10: Foreign or military failure – The incumbent administration suffers no major failure in foreign or military affairs.
Likewise, Mr. Obama hasn’t suffered a major failure overseas yet. (Although Afghanistan is not looking too good these days.) This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 11: Foreign or military success – The incumbent administration achieves a major success in foreign or military affairs.
But neither has Mr. Obama achieved a major success overseas. This statement is FALSE.
___________________
Key 12: Incumbent charisma – The incumbent-party candidate is charismatic or a national hero.
Mr. Obama certainly fits the definition of “charisma” to the word. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
Key 13: Challenger charisma – The challenging-party candidate is not charismatic or a national hero.
Although this could change, the current crop of Republican candidates doesn’t look very charismatic. This statement is TRUE.
___________________
All in all, the Democrats end up holding nine keys out of thirteen (they need seven to win). Four statements are false or unknown; nine are true. Under Mr. Lichtman’s system, then, Mr. Obama looks set to win re-election in 2012.
Of course things might change and get worse for Democrats. The Republicans might nominate somebody like Senator Scott Brown, who is readily equipped with charisma – winning the “challenger charisma” key. Afghanistan might turn into Mr. Obama’s military failure, making him lose that key. The Obama administration might become engulfed in scandal and lose another key.
On the other hand, things might also get better. The economy might be growing steadily come 2012, for instance winning Democrats that key. Mr. Obama might miraculously create peace between Israel and Palestine, winning another key.
But whatever changes happen, Mr. Lichtman’s system gives Democrats surprisingly bright prospects in the 2012 presidential election. Democrats are quite gloomy nowadays, but come November 2012 their spirits may be a bit brighter.