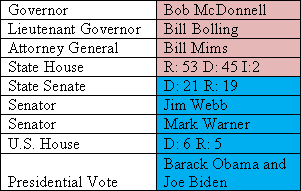
This is the second part of a series of posts analyzing the swing state Virginia. It will focus on Republican Virginia. The third part can be found here.
History
After the Civil War, Virginia constituted a reliable Democratic stronghold. Conservative Democrats such as Harry F. Byrd, who controlled the state’s politics for decades, typified the state’s politicians.
Like many southern states, Virginia enacted a strict set of voting restrictions which successfully disenfranchised blacks. However, it never voted as overwhelmingly Democratic as the Deep South; only one Democrat (FDR) ever won more than 70% of the vote.
Earlier than most Southern states, Virginia began moving Republican, beginning in 1952 (when it cast the ballot for General Dwight Eisenhower). Republican strength rested upon the mountainous west (Republican even in the days of the Solid South) and the fast-growing, Republican-leaning suburbs. The west still votes Republican, but the suburbs are changing fast.
More below.
Republican Virginia
Like many states in the South – and, in fact, like America itself – the “normal” voter usually leans Republican. When one imagines a Virginian (perhaps a hard-scrabble Appalachian type or a white suburban businessman), one is usually looking at a conservative. It is the growing numbers of “other” voters in the state that are making it competitive today.
These Republicans have several factors in common. Exit polls of the 2008 presidential election provide an interesting but incomplete picture of who they are. As is true of the United States in general, Virginia Republicans are predominately white (60% voted for Senator John McCain, versus 55% nationwide). White college graduates are substantially more Democratic than white non-graduates, but polling did not reveal an income gap. Evangelism Evangelicalism constituted a major factor: white evangelicals voted for McCain by a 4-1 margin. Interestingly, white women did not vote much more Democratic than white men; Virginia’s gender gap was quite narrow relative to the nation at large.
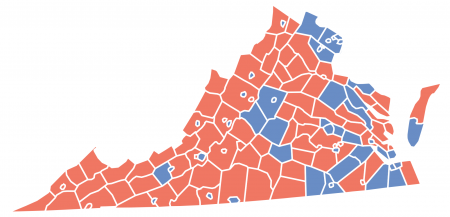
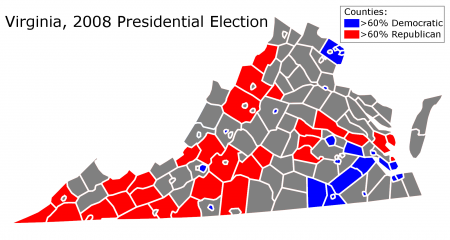
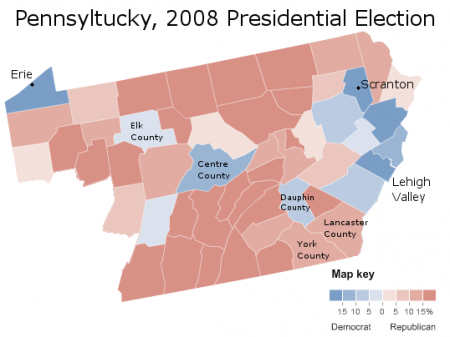
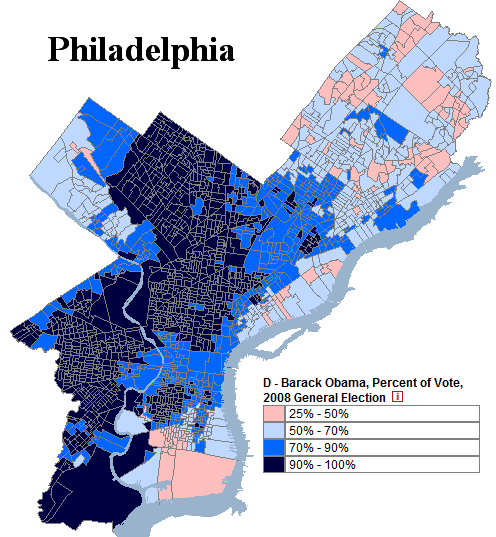
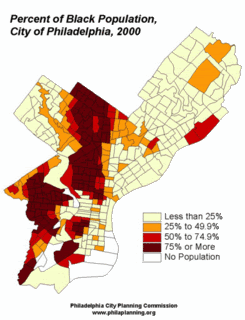
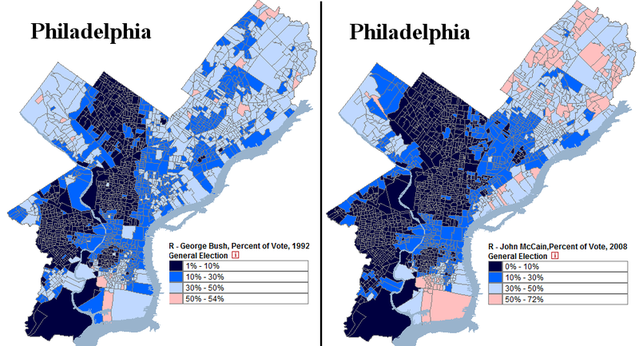
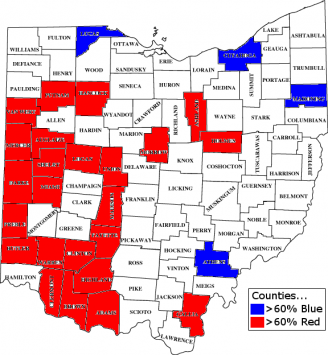
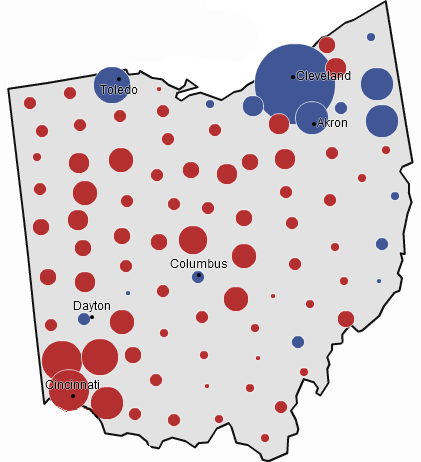
As the map above indicates, the Republicans do best in the western reaches of Virginia. Partly this is because Democratic-voting minorities – mostly blacks – generally live in the east. The quick rightward drift of Appalachian America also accounts for Republican strength, which is growing in the region.
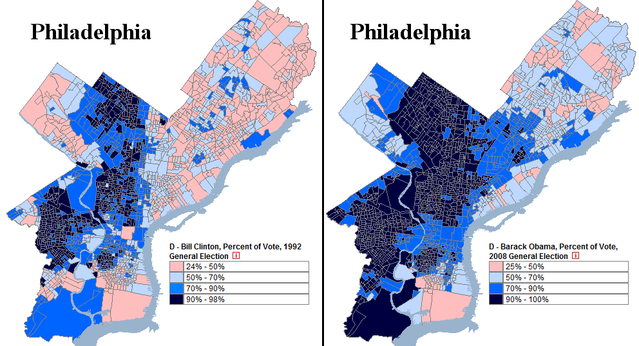
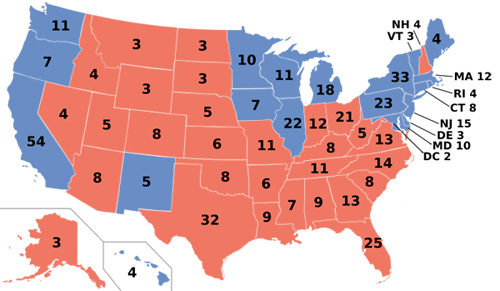
Republicans also retain strength in Virginia’s suburbs and exurbs. Specifically, suburban Richmond and Hampton Roads used to vote Republican quite strongly, ensuring Republican victories even when Democrats undercut their margins in rural Virginia. President Bill Clinton, for instance, did quite well in rural Virginia; it was his losses in these places (Chesterfield and Virginia Beach counties) that kept the state red.
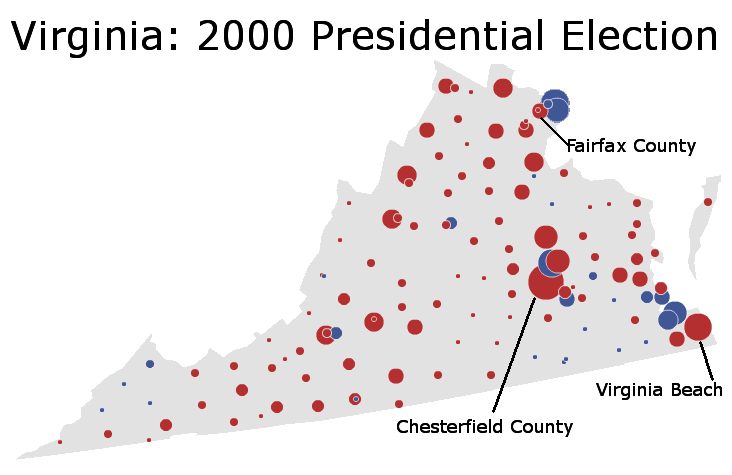
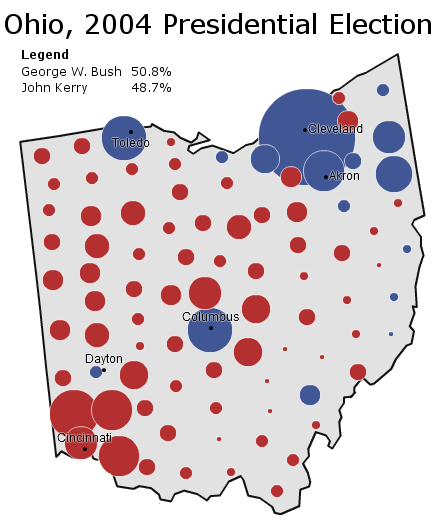
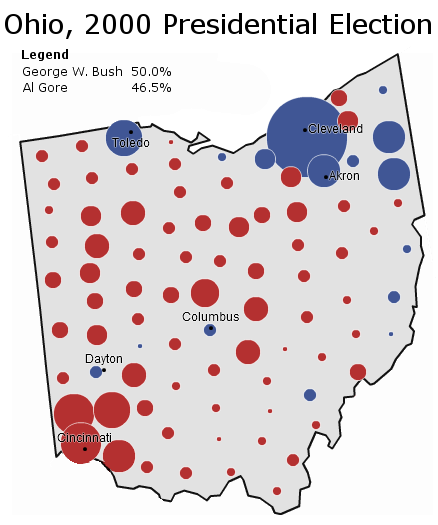
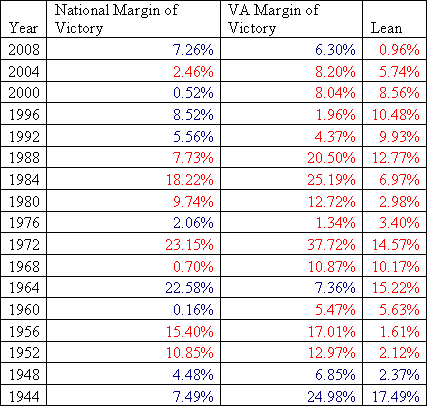
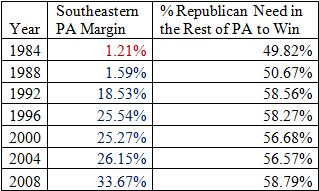
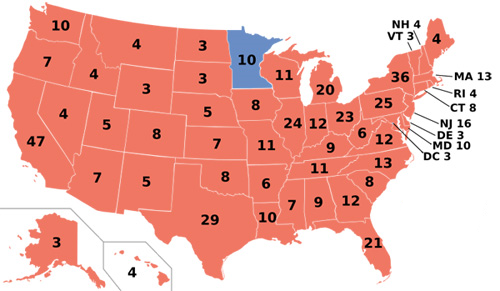
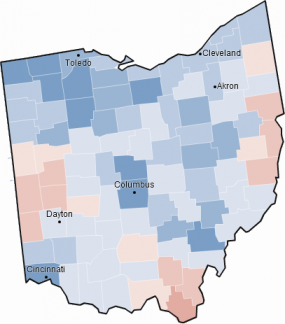
The 2000 presidential election provides an illuminating illustration of Republican Virginia at a strong point:
In that election, Vice President Al Gore lost the state by 8.04% while barely winning the nationwide popular vote. Unlike Mr. Clinton, he was crushed in both rural and suburban Virginia. The former was quickly drifting right, while the suburb’s movement left had yet to materialize.
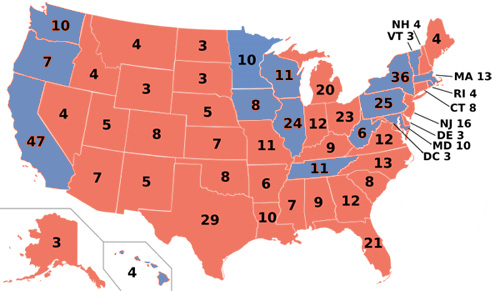
Since that time, of course, things have changed. While Democratic candidates previously – and mostly unsuccessfully – attacked the rural component of Republican Virginia, they have since switched their focus to populous, wealthy, and diverse suburban Virginia. In particular, Democrats have been appealing quite effectively to the suburban NoVa metropolis, which never really fell in love with Republicanism.
–Inoljt, http://mypolitikal.com/